our business

Creating Materials
That Power
the Next-Generation
Energy Society
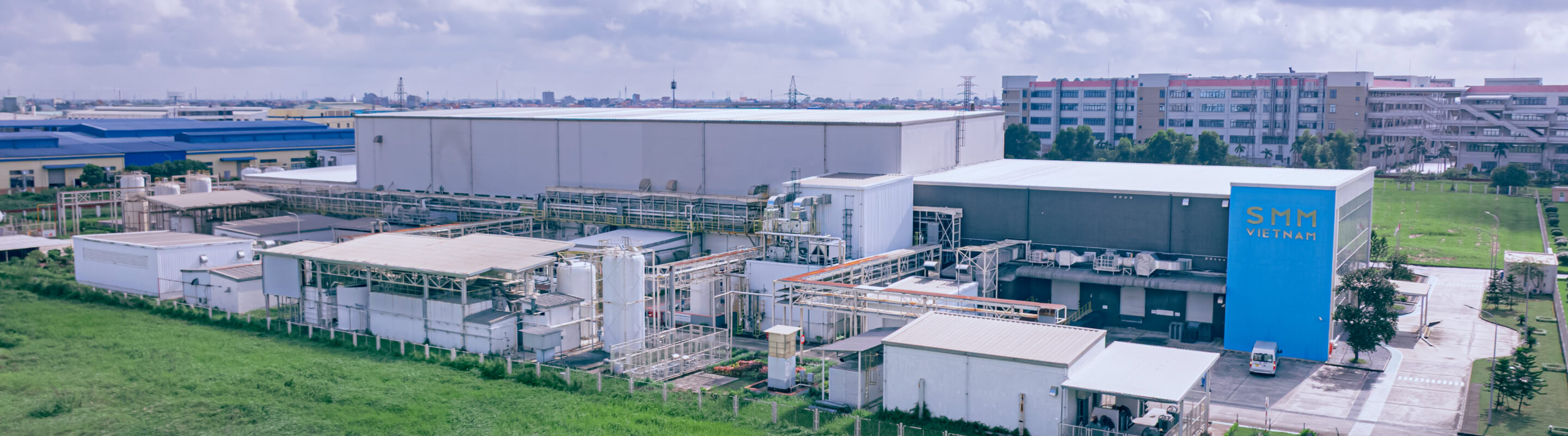
SMM VIETNAM manufactures and sells lithium iron phosphate (LFP),
a cathode material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).
As mobility becomes increasingly electrified and renewable energy underpins social infrastructure,
we contribute to building a sustainable society through LFP.
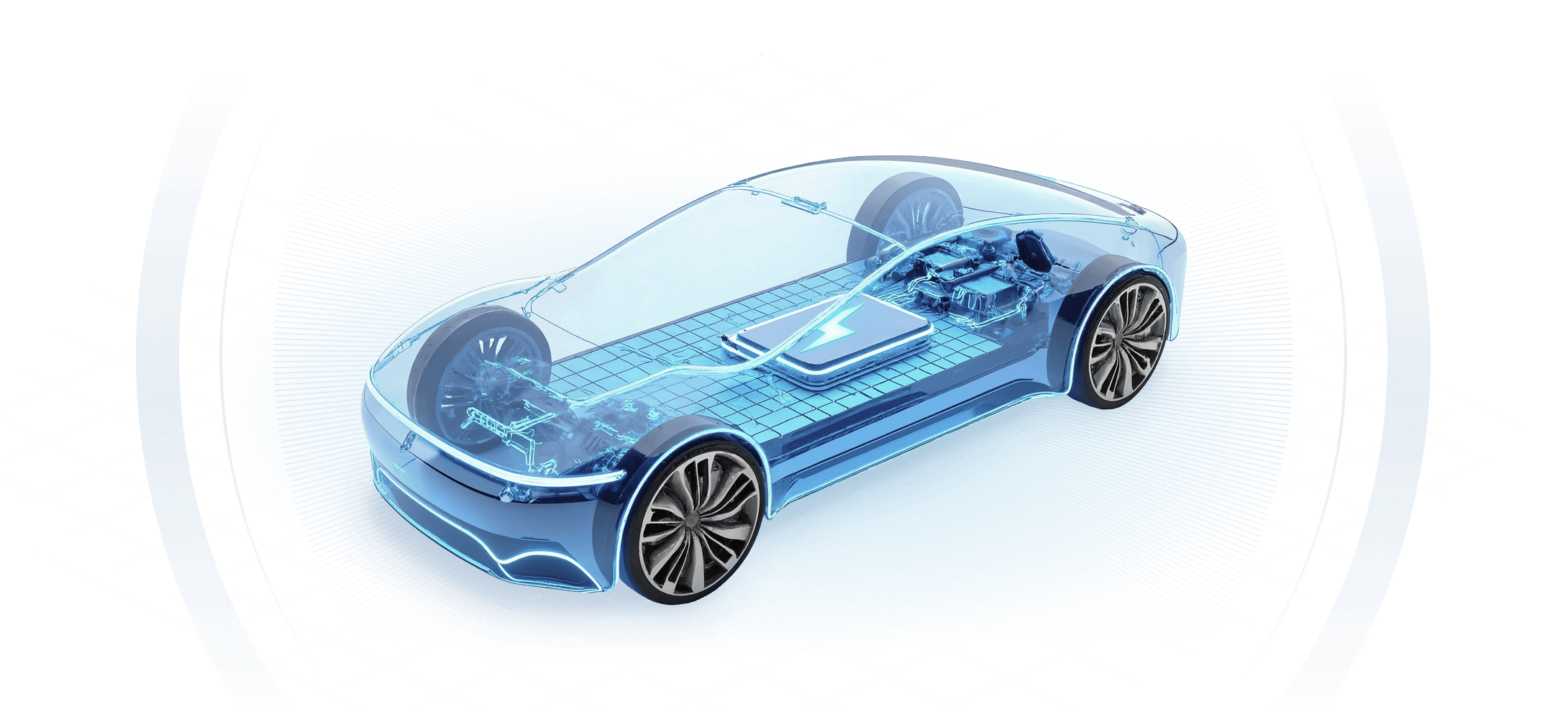
What Are LFP Batteries
and
Cathode Materials?
What Is an LFP Battery
LFP batteries (lithium iron phosphate batteries) are a type of lithium-ion battery that use lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as their cathode material.

Features
Cost-Effective
Does not use rare metals
like cobalt or nickel,
making it inexpensive to produce.

Safe
Low risk of ignition,
offering
high safety.

Long-Lasting
Long battery life and
durability.

Main
Applications
Electric vehicles (EVs)
Stationary energy
storage systems
What Is a Cathode Material
Cathode materials are used in the positive electrode of lithium-ion batteries and play a critical role in
determining battery performance.
SMM VIETNAM
LFP Cathode Material

Battery Manufacturers
LFP cathode material with binder is
coated on both sides of aluminum foil.
Aluminum foil

Why
LFP Batteries Now?
Global Market Size of LFP
Batteries
2024
19.07
billion USD
2032
124.42
billion USD
Compound
Annual
Growth
Rate (CAGR)
25.62 %
Background
- Does not use rare metals such as cobalt and nickel, reducing resource risks and lowering costs
- Minimal fire risk and enhanced safety
- Expanded usein EVs, hybrid vehicles, and buses
- Rising demand for energy infrastructure solutionslike stationary batteries
Differences Between
LFP Batteries
and Other Batteries
LFP
(Lithium IronPhosphate)
NMC
(Nickel Manganese Cobalt)LCO
(Lithium Cobalt Oxide)Safety
Stable with low
risk of fire
Relatively safe, but sensitive to heat
Unstable at high temperatures
Cost
Low cost
(no rare metals)
Includes expensive materials like cobalt
Highly dependent
on cobalt
Lifespan
(Charge Cycles)
Long lifespan
(2,000+ cycles)
Around
1,000–2,000 cycles
Relatively short
Energy Density
Moderate
High
Very high
Main Applications
storage systems
power tools, e-bikes
cameras
Swipe left or right to view the content

